Alibaba Shanghai Campus / Foster + Partners, Innovation
- Mark Lafond, RA

- Sep 23, 2025
- 5 min read
Sustainable Change Models of Innovation

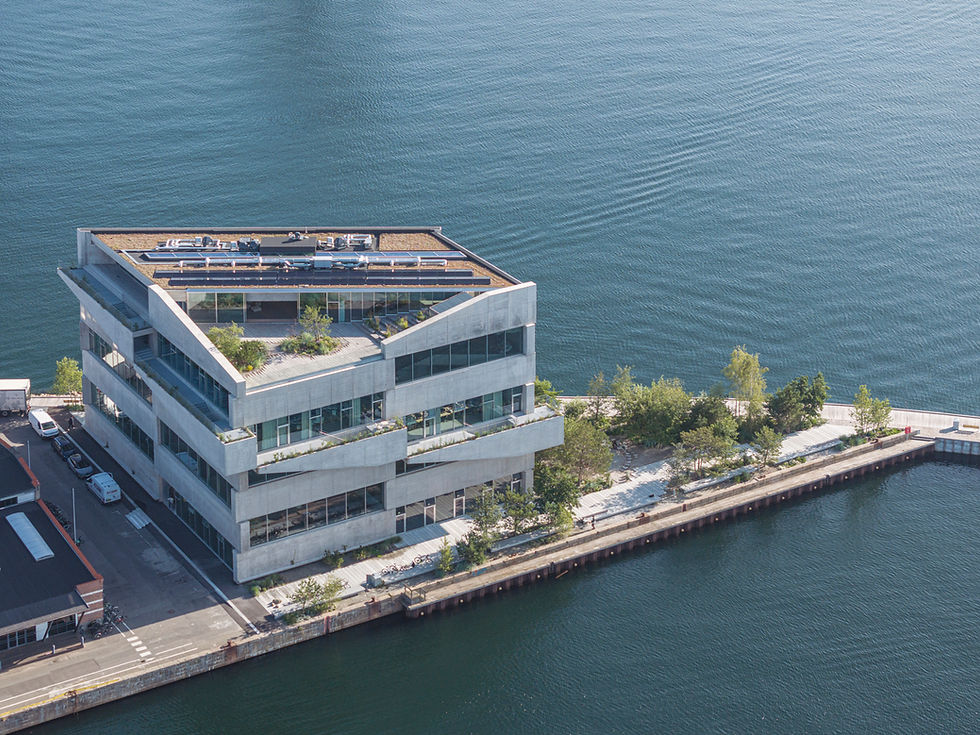
The Alibaba Shanghai Campus, designed by Foster + Partners, is one of the most ambitious corporate architecture projects completed in China in recent years. Located in the Xuhui Riverside district of Shanghai, the project was envisioned as a workplace of the future—one that integrates sustainability, smart technologies, advanced construction techniques, and a strong connection to both the surrounding city and natural environment. Completed in 2024, the campus reflects Alibaba’s status as one of the world’s leading technology companies, combining architectural innovation with a design ethos rooted in flexibility, collaboration, and employee well-being.
The development was designed not merely as a headquarters but as a “living ecosystem.” The campus incorporates cutting-edge smart building technologies, advanced digital design tools, and biophilic principles to create a workspace that promotes both human productivity and ecological responsibility. The project also stands out for its pioneering use of algorithm-driven massing studies, modular construction techniques, and sustainable building strategies, placing it at the forefront of contemporary architecture in Asia.
Architectural Features and Design
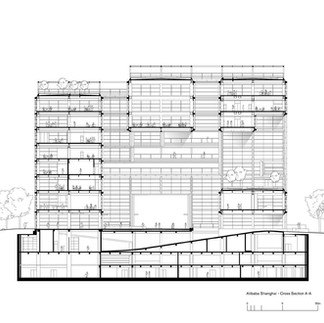
At the heart of the Alibaba Shanghai Campus is an “urban room,” a central public courtyard that serves as the social and cultural core of the development. This large, open space links the multiple wings of the campus and provides a civic-like forum where employees and visitors can meet, collaborate, and enjoy the views of the Huangpu River.
Transparency and openness are key design drivers. Large glass façades provide daylight penetration into the interior, while terraces and landscaped spaces establish a strong visual and physical connection with the outdoors. These terraces cascade along the building edges, offering panoramic views of both the riverfront and the Shanghai skyline, including the Pudong CBD.
The spatial layout was conceived to reflect Alibaba’s corporate culture of adaptability and dynamic teamwork. The floorplates are modular and highly flexible, allowing spaces to be reconfigured according to project needs, team sizes, and departmental structures. The inclusion of winter gardens, roof terraces, and indoor-outdoor transition areas reinforces the emphasis on creating a workplace that is both adaptable and humane.
Technologies and Design Innovations
One of the most groundbreaking aspects of the project was its use of genetic algorithms during the design process. Foster + Partners employed computational modeling to evaluate thousands of design permutations, with objectives ranging from maximizing environmental performance to optimizing views, minimizing energy loads, and enhancing circulation patterns. The resulting form was then fine-tuned through manual architectural refinement, leading to the distinctive cascading profile of the finished building.
Another major innovation lies in the project’s construction methodology. The campus utilized off-site prefabrication and modular assembly techniques to streamline the building process, improve safety, and reduce waste. A particularly notable achievement was the hydraulic lifting of a massive 50-meter spanning structure into place. This process relied on the building’s own steel framework for support, minimizing reliance on cranes and allowing for safer, more efficient construction even under COVID-19 restrictions.
Digital technologies were central to the delivery of the project. Advanced Building Information Modeling (BIM) was used extensively by contractor Shimizu Corporation to manage complex geometries, coordinate between international teams, and ensure precision in assembly. The integration of BIM also enabled the seamless incorporation of sustainable and smart systems into the design.
Sustainability and Smart Building Features
Sustainability was a core consideration throughout the project. The campus achieved LEED Gold certification as well as a 2-Star China Green Star rating, highlighting its environmental credentials.
The design prioritizes natural ventilation, with operable windows and airflow strategies incorporated into every workspace. This reduces dependence on mechanical cooling and improves indoor air quality, directly contributing to employee health and well-being. The central urban room itself is climatically responsive, designed to remain comfortable year-round by shielding occupants from extreme heat or wind.
Energy efficiency is enhanced through a combination of passive design features, high-performance glazing, and advanced shading systems. The building envelope was engineered to balance daylighting with thermal performance, reducing cooling loads during Shanghai’s hot summers while maintaining transparency and connection with the outdoors.
The project also embraces biophilic design. Green terraces, landscaped outdoor spaces, and vegetated rooflines connect employees with nature while improving urban biodiversity. These features also reduce the heat island effect, enhance stormwater management, and contribute to the overall ecological footprint of the development.
On the smart building side, the Alibaba Shanghai Campus incorporates a fully integrated building management system (BMS). This system links HVAC, lighting, security, and energy monitoring into a single, data-driven platform. By leveraging real-time data, the BMS allows operators to optimize energy consumption, detect inefficiencies, and enhance workplace comfort.
In line with Alibaba’s role as a technology company, the campus also features smart campus services designed to improve user experience. Although detailed information on the digital layer remains proprietary, it is understood that the building incorporates IoT sensors, automation tools, and AI-assisted platforms that manage everything from access control to workspace utilization.
Workplace Innovations and Cultural Integration
The design reflects Alibaba’s vision of the workplace as a cultural hub, rather than a purely functional environment. The emphasis on collaboration is evident in the extensive provision of communal spaces, ranging from informal lounges to large multipurpose areas designed for gatherings, lectures, or cultural events.
The incorporation of winter gardens and roof terraces provides employees with access to green spaces at multiple levels, reinforcing the idea that nature should be seamlessly integrated into everyday work life. The cascading terraces also act as “social bridges,” encouraging interaction and informal meetings across different departments.
Flexibility is another key theme. The modularity of the interior spaces allows teams to expand or contract their work environments, reflecting the fast-paced and constantly evolving nature of the tech industry.
The campus was also designed with inclusivity in mind. By emphasizing transparency, accessibility, and openness, the building reflects Alibaba’s ethos of connectivity—not only within its workforce but also with the wider Shanghai community.
Construction and Engineering Achievements
The construction of the Alibaba Shanghai Campus was itself a feat of engineering innovation. Off-site modular construction reduced waste and shortened construction timelines. The hydraulic lifting of the pre-assembled span represents one of the most advanced techniques of its kind in China, highlighting the project’s role as a leader in construction innovation.
The collaboration between Foster + Partners, Shimizu Corporation, and Alibaba exemplified global teamwork in the face of logistical and pandemic-related challenges. Sophisticated digital tools were critical to coordinating between design and construction teams across multiple countries.
Conclusion
The Alibaba Shanghai Campus is a milestone in corporate architecture. It embodies the convergence of architecture, technology, and sustainability, presenting a new paradigm for how workplaces can function as living ecosystems. By combining algorithm-driven design, smart building systems, biophilic principles, and advanced construction strategies, Foster + Partners has created a campus that is both visionary and practical.
This project not only enhances Alibaba’s corporate identity but also sets a global benchmark for the future of office architecture. It demonstrates how workplaces can be designed to optimize human well-being, embrace sustainability, and integrate smart technologies—all while maintaining a strong dialogue with the city around them.
Construction Costs and Specifications
Architect: Foster + Partners
Client: Alibaba Group
Location: Xuhui Riverside, Shanghai, China
Completion: 2024
Certifications: LEED Gold, China Green Star 2-Star
Construction Techniques: Off-site modular construction, hydraulic lifting of large spans
Design Technologies: Genetic algorithms, BIM integration
Notable Features: Urban room courtyard, cascading green terraces, winter gardens, smart BMS integration
Construction Cost: Not publicly disclosed as of 2025
Works Cited
“Alibaba Shanghai Campus / Foster + Partners.” ArchDaily, 10 Sept. 2024.
“Alibaba Shanghai Campus.” Foster + Partners Projects.
“Foster + Partners selected to design Alibaba’s new, algorithm-guided Shanghai HQ.” Archinect, 8 Jan. 2020.
“Innovation through technology: genetic algorithms.” Foster + Partners News, 16 Sept. 2023.
“Alibaba Shanghai Campus.” Better Future Awards.
“Oficinas de Alibaba en Shanghai.” Arquitectura Viva, 2024.
_______________________________________________________________________________






































Comments